As cloud computing becomes integral to modern business operations, 82% of enterprises report cost savings from their transition to the cloud.
While cloud computing offers cost savings, managing these costs can be difficult. Traditional IT systems often waste money due to having too many overused or underused resources. Cloud cost models are built to tackle these issues, ensuring businesses only pay for what they need.
The shift from traditional IT to cloud-based models introduces several financial challenges:
- First, it transforms fixed IT costs into variable ones, complicating budget forecasts.
- Second, without effective cloud pricing models, organizations risk paying for resources they don’t use, draining financial resources.
- Third, while beneficial, the cloud’s scalability feature can lead to cost unpredictability if not adequately managed.
Cloud cost models are crucial. They ensure organizations pay only for what they use, promoting significant cost efficiency. Understanding and strategically implementing these cost models is essential for maximizing the financial benefits of cloud computing, enhancing budget management, and improving operational efficiency.
This blog will explore the most important aspects of cloud cost models, their types, pros and cons, and strategic implementation to help organizations optimize their cloud expenditures effectively.
Understanding Cloud Cost Models
Cloud cost models explain how cloud service providers (CSPs) charge for their services. These models are vital in helping businesses plan their budgets and decide how much to spend on cloud resources, affecting their overall cloud strategy and efficiency.
Cost modeling involves examining the type of resources, how long they are used, and where data centers are located. This analysis helps companies manage their cloud spending more effectively, improving resource allocation and cost-efficiency.
The Importance of Cloud Cost Models in Cloud Computing
Cloud cost models are integral to the strategic deployment of cloud services.
- They help organizations understand and predict expenses, enabling better financial planning and resource allocation. Given the dynamic nature of cloud computing, this understanding is crucial, where factors like demand, supply, and competitive pricing influence costs.
- For instance, using reserved cases can lead to savings of about 72% compared to on-demand pricing. This alignment between cost and consumption prevents financial waste and allows for better budget planning and resource allocation, optimizing cloud services’ financial and operational aspects.
Types of Pricing in Cloud Cost Models
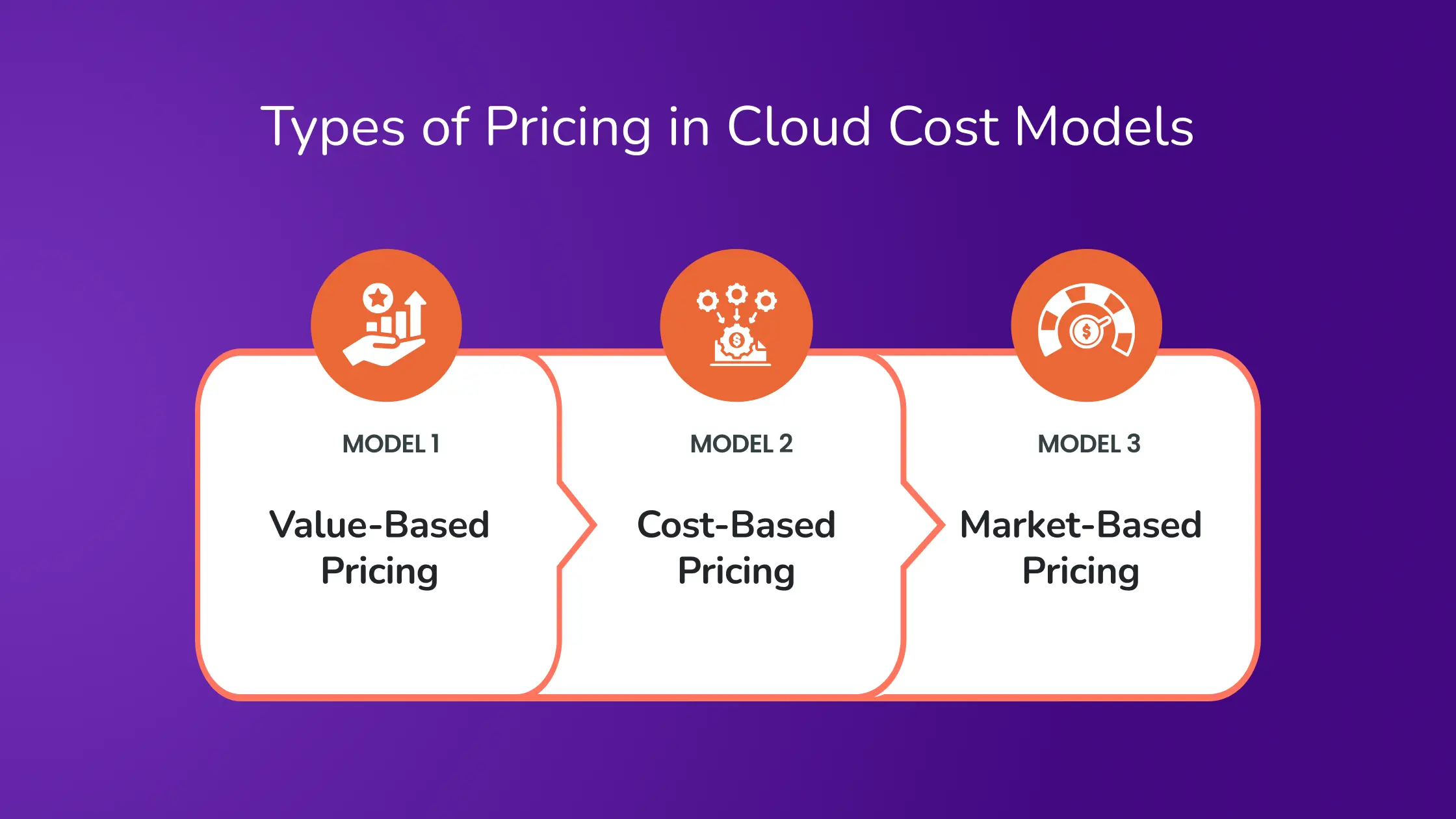
Understanding different pricing helps businesses choose the most suitable model based on their specific needs:
- Value-Based Pricing: Prices are set based on the perceived value of the service to the customer, driven primarily by demand.
- Cost-Based Pricing: This approach is influenced by the service’s cost, with prices often reflecting the underlying expenses involved in providing the cloud resources.
- Market-Based Pricing: Competitive forces and the balance of supply and demand dictate this pricing model, making it essential for businesses to stay informed about market trends.
Components in Cloud Computing Services
When using cloud computing services, your costs are primarily determined by compute power, network usage, and storage needs. Here’s a simple breakdown of each:
- Compute Power: Cloud service providers offer various compute instances, basically different memory and processing power packages. Some instances also include specialized features like enhanced networking or graphics acceleration. The cost depends on how many instances you use, their type, and how long you use them.
- Network Usage: Costs in this category are based on how much data you send to and from the cloud. Most providers charge for data transfer, and you might also pay extra for network services like dedicated IP addresses, network gateways, or load balancers.
- Storage: Providers typically offer different storage services you can choose based on your needs. For example, with elastic storage services, you pay for each gigabyte of storage you use per month.
Cloud Cost Models for Cost Optimization

Cloud cost models are essential tools for businesses looking to optimize their cloud spending. These models provide structured ways to manage and forecast cloud service expenses, ensuring that companies only pay for their needed resources. Let us explore each type of cloud cost model in detail:
I. Pay-As-You-Go Cloud Cost Model
The Pay-As-You-Go model charges cloud service users based solely on their resource usage. This includes computing power, storage, and network services used over a specific period. Customers pay for the exact amount of cloud resources they utilize without purchasing pre-allocated packages or committing long-term.
Why Choose the Pay-As-You-Go Model?
This model offers unparalleled flexibility, allowing businesses to adjust their resource consumption based on current needs in real-time. It’s particularly advantageous for managing fluctuating demands without incurring unnecessary costs or committing to more resources than required.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the On-Demand Model
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Flexibility: Easily scale resources up or down based on immediate needs. | Higher Long-Term Costs: This may become more expensive over time compared to models that offer discounts for long-term commitments. |
| No Upfront Costs: Eliminates the initial investment barrier, making it easier to start with cloud services. | Less Predictability in Spending: Fluctuating costs can make financial planning challenging for variable workloads. |
| Predictable Billing: Offers clear visibility into usage and spending, simplifying budgeting and financial planning. | |
| No Commitment: Frees businesses from long-term contracts or commitments, providing greater operational flexibility. |
Best Practices for Managing Costs with This Model
- Monitor Usage Continuously: Regularly check how much you use and adjust to avoid wasteful spending.
- Set Budget Alerts: Configure alerts to be notified when spending approaches or exceeds your budgeted amount.
- Utilize Cost Management Tools: Tools like AWS Cost Explorer or Google Cloud Billing can help track and manage expenses effectively.
- Optimize Resource Usage: Implement auto-scaling and other resource optimization methods to ensure resources are only used when necessary.
Best Fit For:
- Short-term Projects: Ideal for projects with a limited duration that might require rapid scaling.
- Development and Testing Environments: Enables developers to spin up and tear down environments as needed without long-term financial implications.
- Experimental Projects: Supports innovation by allowing experimentation without the risk of high upfront costs.
- Unpredictable Workloads: Accommodates sudden spikes in demand efficiently.
- Variable Workloads: Useful for businesses with workloads that do not have predictable patterns.
Examples of the Pay-As-You-Go Model:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): Offers flexible pay-as-you-go pricing for over 160 cloud services. Customers pay for each minute or hour of instance use.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP): Provides on-demand pricing, allowing customers to pay by the second for the computing resources they use, with no upfront fees.
II. Subscription-Based Cloud Cost Model
The subscription-based model involves customers paying in advance for cloud services and securing a predefined package of resources for a set period. This model typically offers different pricing tiers, influenced by the subscription duration; longer commitments often result in lower monthly costs.
Why Choose the Subscription-Based Model?
This model provides stability in billing and ensures consistent service availability without the need to manage daily or monthly usage fluctuations. It’s particularly useful for businesses with predictable needs that prefer budgeting their expenses in advance.
Advantages and Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Cost Predictability: Easier budget management due to fixed monthly or annual costs. | Less Flexibility: Changes in service needs might lead to underutilization of resources or the need for plan adjustments. |
| Discount Opportunities: Longer commitments often come with considerable discounts. | Potential for Overpayment: Paying for unused resources if the estimated usage exceeds actual needs. |
| Simplicity in Management: Less need to continuously monitor and adjust resource levels. |
Best Practices for Managing Costs with This Model
- Accurate Needs Assessment: Carefully evaluate your resource needs before committing to a subscription to avoid paying for unused services.
- Review and Adjust Subscriptions Regularly: Monitor service usage and adjust your subscription plan at renewal periods to align with actual needs.
- Take Advantage of Discounts: Negotiate with providers for the best terms on long-term commitments, especially if your organization qualifies for high-spend discounts.
Best Fit For:
- Stable Workloads: Ideal for operations with predictable and consistent resource needs.
- Long-Term Projects: Projects expected to run for an extended period can benefit from lower cumulative costs.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS) and Software as a Service (SaaS): Due to bundled pricing, businesses using these services often find subscriptions cost-effective.
- High-Spend Customers: Organizations with significant cloud expenditures might access corporate discounts through subscription plans, enhancing cost savings.
Examples:
- Microsoft Azure: Offers an Enterprise Agreement that allows larger organizations to commit to a consistent monthly spend in exchange for discounted rates across their service portfolio.
III. Reserved Instances
Reserved Instances (RIs) are a pricing model that cloud service providers offer, where customers commit to using a specified amount of cloud resources for a fixed period, typically one or three years. In exchange for this commitment, customers receive a substantial discount on their cloud service usage compared to standard pay-as-you-go rates. This model is ideal for stable, predictable workloads that require consistent resource availability over time.
Why Use Reserved Instances?
Opting for Reserved Instances can lead to significant cost savings, especially for long-running applications and stable workloads. By committing to a specific usage level, companies can plan their budgets more effectively and take advantage of lower pricing tiers.
Advantages and Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Cost Savings: 50-75% discounts compared to on-demand rates make this a cost-effective option for eligible use cases. | Reduced Flexibility: Committing to a long-term contract minimizes the ability to adapt to changing business needs. |
| Budget Predictability: Fixed costs over the contract period simplify financial planning. | Risk of Overcommitment: Possible financial losses if the reserved capacity exceeds actual usage. |
| Resource Assurance: Guarantees resource availability for the term. | Upfront Costs: Some plans may require a significant initial investment, impacting cash flow. |
Best Practices for Managing Costs with This Model
- Accurate Demand Forecasting: Conduct thorough analyses of your resource needs to prevent over or under-committing.
- Regular Reviews and Adjustments: Periodically reassess your commitments and adjust your reserved instances.
- Utilize Management Tools: Leverage tools offered by cloud providers like AWS Cost Explorer to track and optimize your investments.
- Combine with Other Pricing Models: Use a mix of reserved, on-demand, and spot instances to balance flexibility and cost-efficiency.
Best Fit For:
- Stable Workloads: Suitable for applications with predictable performance demands.
- Long-term Projects: Ideal for deployments expected to be active for several years.
- Mission-Critical Applications: Ensures resource availability for crucial operations.
- Predictable Usage Patterns: Maximizes cost savings for consistent and predictable resource utilization.
Examples
- Amazon EC2 Reserved Instances: AWS offers these, allowing businesses to reserve cloud capacity and choose various payment options to balance upfront payments and total discounts.
IV. Spot Instances
Spot instances provide a cost-effective solution for utilizing unused computing capacity offered by cloud providers at significantly reduced rates, often up to 90% less than standard pay-as-you-go pricing. These instances are available temporarily and can be preempted (interrupted) with little to no notice, depending on demand and price changes.
Why Use Spot Instances?
The primary attraction of spot instances is the potential for substantial cost savings on computing resources. They allow organizations to tap into excess cloud capacity at a fraction of the usual cost. However, spot instances require flexibility regarding when and how computing tasks are executed, as these instances are not guaranteed to be available consistently.
Advantages and Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Cost-Effectiveness: Drastically reduces the cost of cloud computing. | Unpredictability: Instances can be terminated unexpectedly, which may not be suitable for critical workloads. |
| Scalability: Enables handling of higher workloads by accessing more resources without a proportional increase in cost. | Complexity in Management: Requires more sophisticated architecture and management strategies to utilize spot instances effectively. |
Best Practices for Managing Costs with This Model
- Design Fault-Tolerant Systems: Ensure applications and workflows can handle interruptions by incorporating automatic checkpoints and restarts.
- Implement Auto Scaling: Use autoscaling to adapt to the availability of spot instances and maintain performance levels.
- Monitor Performance and Costs: Use cloud management tools to track instance performance and costs and optimize the use of spot instances.
- Prioritize Non-Critical Workloads: Deploy spot instances for non-critical tasks to reduce risks associated with possible interruptions.
Best Fit For:
- Batch Processing and Data Analysis: Tasks that can be paused and resumed without disruption.
- Fault-Tolerant Applications: Applications designed to handle interruptions seamlessly.
- Stateless Web Applications: These are services where user sessions are not stored on the instance itself, allowing for flexibility in instance management.
Examples
- Amazon EC2 Spot Instances: Allows users to bid on spare computing capacity for various applications.
- Google Cloud Preemptible VMs: Offers short-lived compute instances at lower prices for users willing to handle interruptions.
V. AWS Savings Plans
AWS Savings Plans is a pricing model allowing organizations to commit to a specified usage level over a one—or three-year period in exchange for lower prices than on-demand rates.
These plans are divided into three categories:
- Compute Savings Plans,
- EC2 Instance Savings Plans, and
- Amazon SageMaker Savings Plans
each catering to different usage needs.
Why Opt for AWS Savings Plans?
An AWS Savings Plan benefits organizations looking to reduce their cloud computing costs while maintaining flexibility in resource usage. By committing to a certain amount of hourly expenditure, companies can enjoy up to 72% savings over on-demand pricing, which can significantly impact overall IT budgets.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Cost Savings: Significant reductions in cloud computing costs compared to on-demand rates. | Limited Scope: Not applicable to all AWS services, such as Amazon RDS, Redshift, and ElastiCache. |
| Flexibility: Allows savings across different services and regions, depending on the plan chosen. | Long-Term Commitment: Requires committing to one or three years, which could be risky if demand decreases. |
| Simplicity: There is less need to manage or adjust ongoing cloud usage as fluctuations within the commit level do not affect cost. | No Market Resale: These plans cannot be sold on the AWS Marketplace, limiting flexibility in reallocating or recouping costs. |
Best Practices for Managing Costs with AWS Savings Plans
- Conduct Thorough Usage Analysis: Before committing, analyze historical usage data to ensure the plan aligns with actual needs.
- Regular Monitoring and Adjustments: Monitor usage against the plan and adjust coverage as necessary to avoid wastage or underutilization.
- Combine with Other Pricing Models: Use a combination of Savings Plans, Reserved Instances, and On-Demand or Spot Instances to optimize costs across varying workload requirements.
- Strategic Purchasing: Regularly buy Savings Plans in smaller increments to maintain flexibility and alignment with changing needs.
Best Fit For:
- Stable, Predictable Workloads: These are ideal for applications with consistent usage patterns that are unlikely to experience sudden spikes in demand.
- Long-Term Projects: Projects expected to continue for multiple years can benefit from the substantial discounts offered.
- Organizations Scaling Operations: Companies increasing their use of cloud resources can lock in lower rates while growing.
Examples
- Compute Savings Plans: These plans apply broadly across EC2, AWS Lambda, and AWS Fargate usage, providing flexibility in applying savings.
- EC2 Instance Savings Plans: These plans specifically target cost reductions for EC2 instances, offering the deepest discounts for these resources.
- Amazon SageMaker Savings Plans: Tailored for SageMaker, these plans are ideal for organizations heavily utilizing machine learning and data science operations.
AWS Savings Plans offer a balanced approach between cost efficiency and operational flexibility, making them an essential tool for organizations looking to optimize their cloud spending effectively.
Optimize Your Cloud Infrastructure with Avahi’s Expert Services

Transform how you manage and optimize cloud costs with Avahi’s AWS Cloud Cost Optimization Service. Our team of experts helps you reduce the cost of running your cloud infrastructure while enhancing performance and resource utilization.
Harness the power of AWS with Avahi’s specialized services, including AWS Lambda for serverless computing and AWS EC2 for robust Windows server management. Let our certified AWS engineers help you manage and scale your cloud infrastructure efficiently—whether deploying enterprise applications, running high-performance computing (HPC) applications, or building and testing on macOS. With Avahi, you tap into intelligent cloud solutions that minimize costs and maximize performance.
Ready to significantly reduce your AWS costs and optimize your cloud infrastructure?