Managing sensitive data and staying compliant with regulations is a significant challenge in healthcare.
However, cloud computing in healthcare is revolutionizing the system, transforming patient care and making operations more efficient. This technology shift is making healthcare data easier to access, more secure, and simpler to manage despite increasing demands and complex regulations.
Statistics show that cloud computing in healthcare is becoming more popular. By 2029, its market value is expected to reach $120.6 billion, growing at 17.5 % annually. This growth shows that more healthcare providers see the benefits of using cloud technology to improve their services. This shift boosts security and compliance and frees medical staff to focus more on patient care.
In this blog, we will explore how cloud computing shapes healthcare, exploring its impact, benefits, and prospects of this pivotal technology in the medical field.
| What Is Cloud Computing in Health Care?
Cloud computing in healthcare refers to using remote servers, accessible via the internet, to manage, store, and process healthcare data. It differs from on-site data centers that host patient data directly on local computers. By adopting cloud computing, healthcare providers can access critical data from anywhere, facilitating faster and more efficient healthcare delivery. |
Types of Cloud Computing in Healthcare
Cloud computing in healthcare is categorized based on deployment and distribution models, each tailored to meet specific needs regarding accessibility, security, and scalability.
| Model Type | Category | Description | Use Cases in Healthcare |
| Distribution | SaaS (Software as a Service) | Delivers software applications over the internet, eliminating the need for on-premises installations. | EHR systems, patient management systems, telemedicine applications. |
| IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) | Provides virtualized computing resources like servers, storage, and networking over the internet. | Hosting large-scale data applications, genomics research, big data analytics. | |
| PaaS (Platform as a Service) | Offers a platform allowing developers to build, deploy, and manage applications without managing the underlying infrastructure. | Developing custom healthcare applications, collaborative research platforms. | |
| Deployment | Community Cloud | Shared by multiple organizations with similar needs and requirements, often within the same industry or community. | Regional healthcare systems, collaborative projects among hospitals or research institutes. |
| Private Cloud | Dedicated to a single organization and can be hosted on-premises or externally by a third-party provider. Offers enhanced control and security. | Hospitals and healthcare systems handling sensitive data, internal data centers. | |
| Public Cloud | Operated by third-party providers offering scalable resources and services over the internet. | Non-sensitive healthcare applications, cloud-based analytics, patient engagement tools. | |
| Hybrid Cloud | Combines public and private clouds, allowing data and applications to be shared between them. | Balancing need for security (private cloud) and scalability (public cloud), flexible data management. |
Benefits of Cloud Computing in Healthcare
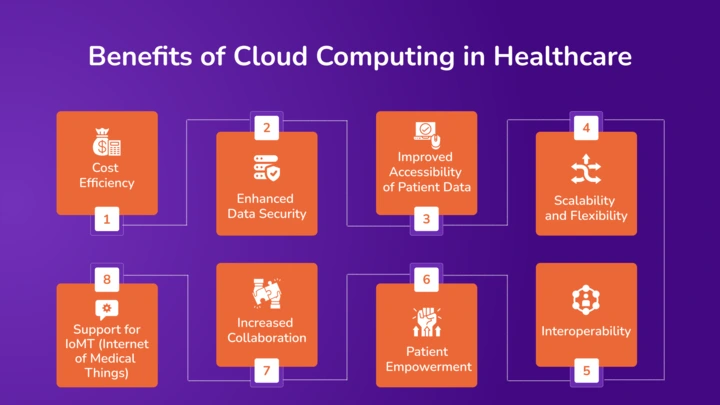
Cloud computing is transforming the healthcare industry by offering scalable, cost-effective, and secure data management solutions. This technology allows healthcare providers to deliver better care efficiently and at lower costs.Here are the benefits of cloud computing in healthcare:
Cost Efficiency
Cloud computing reduces the need for physical data storage and large IT infrastructures, significantly lowering operational costs. Healthcare providers only pay for the resources they use, which can be scaled up or down as needed. This flexibility helps manage costs effectively, especially when patient data volumes fluctuate.
Enhanced Data Security
Advanced security measures cloud service providers provide minimize the risk of data breaches and loss. Cloud platforms are equipped with robust cybersecurity protocols that safeguard patient information against unauthorized access and cyber threats.
Improved Accessibility of Patient Data
Cloud computing enables healthcare professionals to access patient data remotely and in real time, which is crucial for timely decision-making and treatment. This accessibility supports telehealth services and emergency care, enhancing patient outcomes.
Scalability and Flexibility
As healthcare data grows, cloud services can easily scale to accommodate increased storage needs without the upfront costs associated with physical servers. This scalability ensures that healthcare facilities meet the growing demand for digital health services.
Interoperability
Cloud computing allows different healthcare systems to communicate more effectively, allowing for seamless exchange and integration of patient data across various platforms. This interoperability improves care coordination and supports comprehensive health management.
Patient Empowerment
Cloud computing gives patients more control over their health data. They can access their medical records anytime, encouraging active participation in their healthcare processes and better self-management of conditions.
Increased Collaboration
Cloud platforms facilitate better collaboration among healthcare professionals by allowing them to share patient information securely and efficiently. This collaboration is essential for multidisciplinary care teams, leading to more accurate diagnoses and effective treatment plans.
Support for IoMT (Internet of Medical Things)
Cloud computing enables real-time data collection from medical devices, improving patient health monitoring and management. This integration supports proactive health measures and personalized treatment plans based on real-time data analytics.
The Risks of Cloud Computing in Healthcare
Cloud computing offers significant benefits for healthcare, but it also presents specific risks that need careful consideration:
Expertise Shortage
Healthcare organizations often lack the technical expertise to effectively implement and manage cloud systems. Hiring or training staff with these specialized skills is crucial to leverage the full benefits of cloud computing.
Data Security and Privacy
Storing sensitive patient data in the cloud can lead to security vulnerabilities. Despite cloud providers’ robust security measures, the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access remains a significant concern. Healthcare organizations must ensure they have strong security protocols and compliance measures.
Change Management
Transitioning to cloud-based systems requires substantial changes in processes and operations. Effective organizational change management is essential to ensure smooth adoption and minimize staff resistance, maximizing the return on investment.
Compliance Challenges
Healthcare organizations must comply with strict regulations like HIPAA in the U.S. or GDPR in Europe. Maintaining compliance is critical to avoid legal issues and fines and often requires expertise that may not be present internally.
Vendor Lock-In
Relying on a single cloud service provider can lead to dependency, making switching vendors or integrating with other systems difficult. This lack of flexibility can hinder operational efficiency and innovation.
Use Cases of Cloud Computing in Healthcare
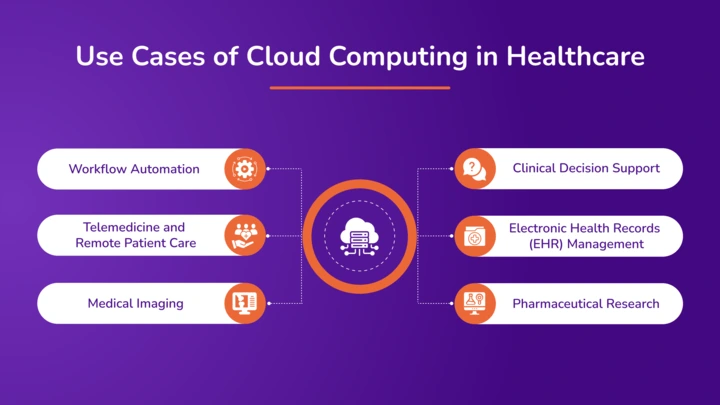
Cloud computing is revolutionizing healthcare by providing scalable, secure, and efficient solutions to manage various patient care and administration aspects. Here are some use cases of cloud computing in the healthcare industry:
Workflow Automation
In hospital management, cloud computing facilitates real-time monitoring of patients and automates supply chain operations. It enables efficient management of medical records, equipment tracking, and scheduling, ensuring that operations run smoothly and reducing the risk of administrative errors. Automation in document management, billing, and reporting frees healthcare professionals to focus more on patient care.
Telemedicine and Remote Patient Care
Cloud-based platforms have expanded telemedicine, allowing patients to consult with doctors remotely. This technology supports video consultations and access to health records, lab results, and prescriptions from anywhere. It is particularly beneficial for monitoring chronic conditions, providing care in remote areas, and conducting remote surgeries, significantly improving patient access to healthcare services.
Medical Imaging
Cloud storage can handle the large volumes of data generated by medical imaging devices. Cloud platforms allow for easier sharing and analysis of images like X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans among healthcare professionals.
Clinical Decision Support
Cloud computing enhances diagnostic accuracy through AI and machine learning. Systems like Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS) consolidate data, aiding healthcare professionals in making precise diagnoses based on extensive, real-time data. This approach reduces misdiagnoses and enhances patient outcomes by using predictive analytics to identify early health risks and trends.
Electronic Health Records (EHR) Management
Cloud-based EHR systems are a pivotal application of cloud computing in healthcare. These systems store and manage patient data, including medical history, medications, and treatment plans, and are accessible from any location. This interoperability helps healthcare providers improve care coordination, streamline workflows, and make informed decisions that enhance patient outcomes.
Pharmaceutical Research
Cloud computing significantly speeds up the drug discovery process by providing powerful computational resources and collaborative tools needed for research. It supports the handling of large datasets and complex simulations and facilitates collaboration among globally dispersed research teams, accelerating innovations in pharmaceutical development.
Real-World Example of Cloud Computing in Healthcare
Below are a few real-world examples that illustrate the transformative role of cloud computing in enhancing healthcare services and patient outcomes.
Pfizer
Pfizer, a leading global pharmaceutical and biotechnology company, leveraged cloud computing in its operations, particularly during the development of the COVID-19 vaccine.
- Partnership with AWS: Pfizer collaborated with Amazon Web Services (AWS) to create a dedicated scientific data cloud (SDC). This partnership allowed for the rapid access and analysis of biotechnological data, which previously took weeks or months.
- Efficient Migration: The company executed one of the fastest cloud migrations for its size, transferring over 1,000 applications and 8,000 servers to the AWS cloud within 42 weeks.
- Cost and Environmental Benefits: This move resulted in significant cost savings of $37 million and a notable reduction in carbon footprint (approximately 4,700).
- Support for Vaccine Development: The availability of advanced cloud computing resources was crucial during the COVID-19 pandemic, particularly in accelerating the analysis stage of vaccine development.
Avahi
A regional healthcare network faced operational delays and inefficiencies in patient billing processes, compounded by slow data processing and frequent system downtimes.
- Solution: Customized AWS infrastructure incorporating Amazon HealthLake for data management and AWS WorkSpaces for a secure, scalable platform.
- Purpose: To enhance the processing and analysis of patient data and insurance claims.
Outcome:
- Results: Achieved a 40% reduction in claim processing time and significantly reduced system downtimes.
- Business Impact: Faster revenue cycles, improved cash flow, and increased patient satisfaction due to quicker billing resolutions.
- Compliance and Security: Ensured HIPAA compliance and enhanced data security and patient privacy through AWS WorkSpaces.
For more insights into Avahi’s transformative impact on healthcare through cloud computing, explore our detailed case studies:
- Fringe Improves Scalability and Security of AWS Infrastructure by Relying on Avahi Expertise in Cloud Architectures
- The Emergency Center Goes to Market with Healthcare Provider Application by Turning to Avahi to Build a Secure AWS Platform That Enables AI Analysis
Transform Your Cloud Experience with Avahi Expertise

Avahi specializes in delivering cutting-edge cloud solutions that address your unique business challenges. As your dedicated AWS Cloud Consulting Partner, we are committed to simplifying your cloud journey through seamless adoption, migration, and application modernization.
Our Services Include:
- Adoption and Migration: Migrate your legacy applications or workloads to AWS for enhanced reliability, scalability, and performance.
- DevOps: Unlock the power of your data with advanced analytics and machine learning capabilities.
- Cloud Staffing Services: Access top-tier talent to support and drive your cloud initiatives, ensuring a seamless and effective cloud transformation.
Want to explore how Avahi can help you simplify, modernize, and excel in your cloud journey?