Payment fraud is increasing worldwide. McKinsey & Company projects that losses from payment card fraud will reach $400 billion over the next decade. With the volume of digital transactions increasing daily, customer expectations are higher than ever.
Organizations are under more pressure than ever to protect customer data. Cardholder information is moving across more systems, platforms, and tools, often in real time.
Whenever a customer makes a purchase, submits personal details, or reaches out for support, sensitive information is exchanged. And as the number of digital touchpoints increases, so does the attack surface.
One area that’s drawing increased attention is AI-powered chatbots.
Once limited to answering FAQs, they now help users check account balances, process orders, and even assist with transactions—often in real time. That convenience is powerful, but it also means that these tools operate closer than ever to sensitive data.
And when that data includes payment information, the rules change.
Any system that touches cardholder data falls under the scope of the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard(PCI DSS). This non-negotiable framework aims to protect consumer data and reduce fraud. Non-compliance doesn’t just mean regulatory trouble—it can mean reputational damage, lawsuits, and heavy financial penalties.
The reality is that most chatbots aren’t built with compliance in mind. Misconfigurations, weak access controls, and insecure API integrations can introduce serious vulnerabilities, often without businesses realizing it.
This blog will explain PCI DSS compliance, how AI chatbots fit into the equation, and what organizations must do to protect their customers, data, and credibility.
PCI DSS Compliance: What Every Organization Needs to Know
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is a set of security standards developed by the Payment Card Industry Security Standards Council (PCI SSC). Its purpose is simple but critical: to ensure that any organization processing, storing, or transmitting credit or debit card data does so securely.
PCI DSS protects cardholder data and reduces the risk of payment card fraud. It applies to all entities that handle card data, regardless of size or transaction volume. This includes:
- Merchants (e.g., retail stores, e-commerce businesses)
- Payment processors
- Financial institutions
- Service providers that interact with card data in any form (e.g., cloud services, chatbot platforms)
Even if you outsource payments to a third-party provider, your organization is still responsible for ensuring the provider is PCI-compliant.
PCI DSS Requirements: What Matters for Chatbots and Digital Interfaces
The current version, PCI DSS v4.0.1, outlines twelve core requirements under six fundamental objectives. Here is a breakdown of the most relevant categories when it comes to AI chatbots and digital systems:
| Objective | Requirement |
| Build and Maintain a Secure Network |
|
| Protect Cardholder Data |
|
| Maintain a Vulnerability Management Program |
|
| Implement Strong Access Control Measures |
|
| Monitor and Test Networks |
|
| Maintain an Information Security Policy |
|
The Cost of Ignoring PCI DSS Compliance
Failing to meet PCI DSS requirements can have serious consequences regarding regulatory fines and long-term financial and reputational impact.
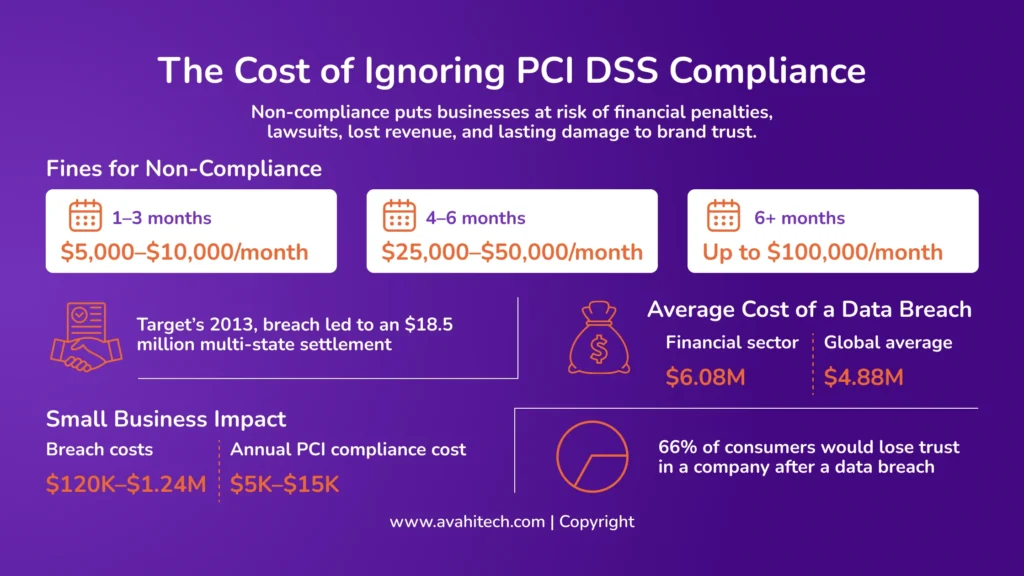
Fines for Non-Compliance
When organizations fall out of compliance, fines can escalate quickly depending on how long the issue goes unaddressed:
- First 3 months: $5,000 to $10,000 per month
- 4 to 6 months: $25,000 to $50,000 per month
- More than 6 months: Up to $100,000 per month
Breach Settlements and Legal Costs
The financial impact of a data breach can be alarming. In the widely publicized Target breach of 2013, the company reached an $18.5 million settlement with 47 states, a reminder of how costly non-compliance can be once cardholder data is compromised.
Average Cost of a Data Breach
The average cost of a data breach in the financial sector is $6.08 million—well above the global average of $4.88 million. These numbers reflect direct losses and the cost of recovery, legal fees, and damage control.
Impact on Small and Mid-Sized Businesses
Smaller companies are especially vulnerable. Data breach costs for small businesses typically range from $120,000 to $1.24 million, enough to threaten the company’s future. Meanwhile, the annual cost of maintaining PCI DSS compliance, including audits, security tools, and employee training, generally falls between $5,000 and $15,000 for mid-sized businesses.
Loss of Customer Trust
The damage doesn’t stop at financial loss. According to research, 66% of consumers say they would lose trust in a company after a data breach. That kind of erosion in customer confidence can lead to long-term revenue and market credibility declines.
Role of AI Chatbots in Payment and Customer Service
Here are some of the common use cases where these chatbots are used:
1. Transaction Processing
AI chatbots are often integrated into websites and apps to help users complete purchases. They can guide customers through the checkout process, suggest payment methods, or provide updates on payment status. Some advanced bots even support payment links or wallet integrations.
2. Account Support
Chatbots handle everyday account-related tasks such as password resets, checking balances, updating contact details, or retrieving order history. This reduces the need for live agents and improves response times.
3. Handling Payment Information
Some chatbots are configured to collect or validate payment information. This can include prompting users to enter credit card details or verifying payment status. However, handling this data type comes with significant security and compliance requirements.
Security Risks of AI Chatbot Deployment
While AI chatbots offer efficiency and cost savings, they also introduce security and compliance risks in payment environments. Without proper controls, these systems can create vulnerabilities that expose cardholder data and violate PCI DSS requirements. Below are three critical risk areas to consider:
1. Data Exposure

Chatbots can collect sensitive payment data when users input card details into unsecured chat interfaces if these inputs are not blocked, filtered, or redirected to a secure channel. The data may be stored or transmitted without proper encryption, increasing the risk of interception, unauthorized access, or leaks.
A study by Verizon’s Data Breach Investigations Report (DBIR) highlights that payment data remains one of the most frequently compromised data types in web application breaches, often due to poor input handling and weak data masking.
2. Weak Authentication
Chatbots that lack strong authentication controls are vulnerable to abuse. Without identity verification mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) or session validation, malicious users can impersonate customers or launch automated attacks to harvest sensitive account data. Weak authentication in chatbot systems makes it easier for attackers to exploit this vector.
3. Insecure Integrations
AI chatbots often rely on APIs to integrate with backend systems, CRMs, payment processors, and databases. These integrations can create new attack surfaces if not securely designed and monitored. Vulnerable or misconfigured APIs can expose sensitive endpoints, allow unauthorized data access, or become a path for injection attacks.
Gartner predicts that by 2025, over 40% of data breaches will be linked to the improper use of AI. This risk is particularly severe in a PCI-regulated environment because API misconfigurations can lead to uncontrolled access to cardholder data or system components.
Compliance Considerations for AI Chatbots
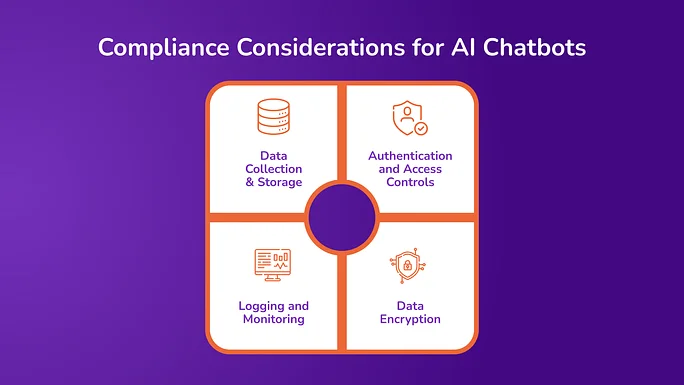
Chatbots AI chatbots interacting with payment systems must align with PCI DSS to avoid compliance gaps. Here are a few compliance considerations that organizations must look into while deploying AI chatbots:
-
Data Collection & Storage
AI chatbots should minimize the collection of sensitive cardholder data. They should collect only the necessary information to complete a transaction or provide a service. Unnecessary data collection increases the risk of exposure and complicates compliance efforts.
Storing cardholder data should be avoided unless it is essential. If storage is necessary, implement strong encryption and access controls. The 2017 Equifax breach exposed data from 143 million accounts, underscoring the consequences of weak data protection and poor security governance. This suspected state-sponsored incident remains one of the most damaging data breaches in history, with long-term financial and reputational impacts still unfolding.
-
Authentication and Access Controls
Access to chatbot systems should be limited based on business needs. Implement role-based access controls (RBAC) to ensure only authorized personnel can interact with sensitive components. Regularly review access logs to detect unauthorized attempts. PCI DSS Requirement 7 emphasizes restricting access to cardholder data by business need-to-know.
Implementing MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring multiple verification forms before granting access. This reduces the risk of unauthorized access due to compromised credentials. PCI DSS Requirement 8 mandates identifying and authenticating access to system components.
-
Logging and Monitoring
Maintain detailed logs of all chatbot interactions and access attempts. These logs are vital for detecting anomalies, investigating incidents, and demonstrating compliance.
Integrate chatbot logs into Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems to enable real-time analysis and correlation with other security events. This holistic view enhances the ability to detect and respond to threats promptly.
- Data Encryption
Encrypt cardholder data during transmission over open, public networks and when stored. Use strong cryptographic protocols to protect data integrity and confidentiality. PCI DSS Requirements 3 and 4 address protecting stored cardholder data and encryption during transmission.
When utilizing third-party chatbot providers, ensure they comply with PCI DSS standards. Conduct thorough due diligence, including reviewing their compliance reports and security practices. PCI DSS Requirement 12.8 emphasizes managing risks associated with third-party service providers.
Common Challenges in Ensuring PCI DSS Compliance with
Deploying AI chatbots in payment and customer service environments introduces several operational and technical challenges. If not proactively addressed, these issues can complicate compliance with PCI DSS.
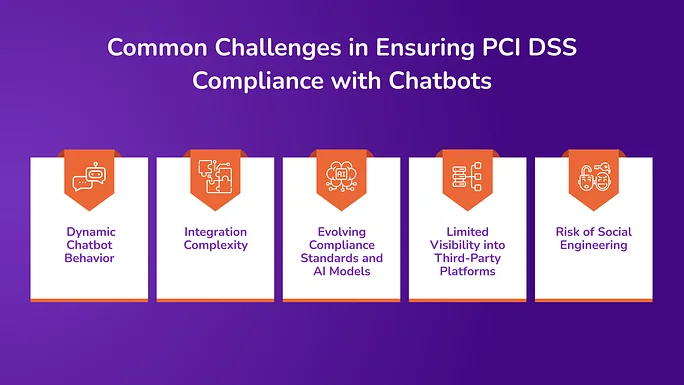
1. Dynamic Chatbot Behavior
AI chatbots, especially those powered by machine learning or natural language processing, can behave unpredictably. Unlike rule-based bots, these models may generate responses based on user input in ways that developers didn’t explicitly program.
This poses a risk when users attempt to enter cardholder data, as the bot might not block or redirect such inputs. Compliance requires strict input validation, output monitoring, and safeguards to prevent unauthorized data collection or disclosure.
2. Integration Complexity
Many organizations still rely on legacy payment systems that are not built to integrate modern APIs or conversational interfaces. Connecting chatbots to these systems securely requires custom middleware, data translation layers, and careful authentication protocols.
This complexity increases the likelihood of configuration errors or insecure connections, which can create compliance gaps. Thorough testing and network segmentation are essential to isolate payment data flows from chatbot interactions.
3. Evolving Compliance Standards and AI Models
PCI DSS standards are updated periodically, and AI technologies evolve even faster. Ensuring ongoing compliance requires constant monitoring of the regulatory landscape and the underlying AI systems.
For example, version 4.0.1 of PCI DSS introduces more detailed requirements around authentication, access controls, and continuous testing. Organizations must adapt chatbot governance frameworks to meet these evolving requirements while updating AI models to reflect changes in business logic or user behavior.
4. Limited Visibility into Third-Party Platforms
Companies using external chatbot platforms (e.g., SaaS providers) often lose visibility into how data is handled, stored, or transmitted on those platforms. Verifying PCI DSS compliance is difficult without clear insight into the third party’s architecture and security controls.
To mitigate this, businesses must conduct due diligence, request detailed compliance documentation (e.g., PCI AOC—Attestation of Compliance), and include security obligations in vendor contracts.
5. Risk of Social Engineering
Chatbots are susceptible to social engineering attacks where malicious users try to manipulate the bot to reveal sensitive data or bypass verification steps. Unlike humans, chatbots lack contextual judgment, making them vulnerable to carefully crafted prompts.
Attackers might use impersonation, credential stuffing, or prompt injection to exploit weakly secured bots. To prevent this, implement strict access controls, input sanitization, session timeouts, and anomaly detection to flag suspicious interaction patterns.
Best Practices for Ensuring PCI DSS Compliance with Chatbots

Below are essential practices that help maintain compliance while minimizing risk.
1. Avoid Direct Card Handling
Chatbots should not be used to collect, process, or store primary account numbers (PANs), expiration dates, or CVV codes. Allowing bots to handle this data increases the attack surface and brings the entire chatbot platform under PCI scope. This adds significant complexity to compliance and introduces unnecessary risk.
Instead, design bots to avoid accepting sensitive inputs. Implement input validation filters that prevent users from entering card numbers or similar patterns. This reduces liability and simplifies compliance.
2. Use Secure Payment Portals
When a chatbot interaction requires a payment, redirect the user to a PCI-compliant, secure payment gateway or hosted payment page. These portals are designed to meet PCI DSS standards and shift the responsibility for card data handling to the payment provider.
Use HTTPS with TLS encryption for all redirections and confirm the destination is PCI certified. Avoid embedding payment fields directly within the chatbot interface.
3. Implement Tokenization Methods
Tokenization replaces sensitive card data with non-sensitive tokens with no exploitable value if intercepted. If your chatbot needs to reference past transactions or saved cards, use tokenized identifiers provided by a payment processor.
This reduces the PCI scope since the card data is never stored or processed within the chatbot or your internal systems. It also improves breach resilience by ensuring that intercepted tokens are useless to attackers.
4. Audit Chatbot Behavior
Perform periodic penetration testing and vulnerability scanning on chatbot systems, especially those integrated with customer accounts or payment flows. These tests help identify misconfigurations, outdated components, and exploitable flaws.
Follow PCI DSS Requirement 11, which mandates regular testing of all system components in scope. Testing should include chatbot APIs, third-party connectors, and any linked backend infrastructure.
5. Train Teams on Security
Ensure that developers building or maintaining chatbots understand the security risks of handling financial and personal data. Training should cover secure coding practices, input sanitization, access control, and compliance principles specific to PCI DSS.
System administrators and operations teams should also be trained to monitor chatbot activity, manage credentials, and respond to security incidents.
6. Document for Compliance Reviews
Keep thorough records of all chatbot configurations, code changes, access logs, compliance tests, and vendor certifications. This documentation supports internal audits and external PCI DSS assessments.
Well-maintained documentation also helps quickly identify control gaps and demonstrates due diligence in case of a breach or data incident.
How Does the Avahi GenAI Platform Automate and Enforce Compliance Standards?
The Avahi AI Platform provides AI-powered features to enhance data security, streamline compliance workflows, and support organizations in meeting PCI DSS 4.0 requirements. Below is a breakdown of how specific features align with relevant requirements.
Data Masking
The Data Masker tool supports compliance with Requirement 7 by masking PCI-sensitive data from users who do not need access to complete cardholder information.
This enforces the principle of least privilege, ensuring that employees or systems only access the data necessary for their role. Data Masker de-identifies information in real time and enables secure role-based data views without compromising operational efficiency.
Smart Summarizer
AvahiGen AI’s ability to process and extract content from .txt, .doc, and .pdf files supports the discovery of unprotected PANs (Primary Account Numbers) across multiple file formats.
When paired with features like Smart Summarizer, this capability enables automated content review and aids in identifying unencrypted cardholder data. This proactive data visibility helps security teams detect and remediate non-compliant storage or transmission practices.
Structured Extraction
AvahiGen’s Structured Extraction capability enables rapid processing and categorizing of documents like KYC forms, loan applications, and compliance records. In the event of a suspected breach, this tool supports the incident response process by quickly surfacing relevant data for investigation, reducing time to resolution, and enhancing audit traceability.
This helps meet the requirement for a well-documented, testable, and ready-to-deploy incident response process.
Role-Based Access Control
Features like Data Masker and Structured Data Extraction imply configurable access management, where different user roles can perform specific operations on data (e.g., view summaries, query CSVs, or mask sensitive elements). This aligns with PCI DSS 4.0 expectations for fine-grained access control and accountability in system operations.
Natural Language Querying for CSVs
With CSV Querying, compliance and risk teams can analyze transactional data or customer records using a secure, AI-assisted interface. This reduces reliance on manual scripts or direct database access, which often carry security risks.
The simplified, controlled interface supports secure analytics without exposing raw data to unnecessary users, reducing development overhead, and minimizing security vulnerabilities.
Discover Avahi’s AI Platform in Action
At Avahi, we empower businesses to deploy advanced Generative AI that streamlines operations, enhances decision-making, and accelerates innovation—all with zero complexity.
As your trusted AWS Cloud Consulting Partner, we empower organizations to harness AI’s full potential while ensuring security, scalability, and compliance with industry-leading cloud solutions.
Our AI Solutions include
- AI Adoption & Integration – Utilize Amazon Bedrock and GenAI to enhance automation and decision-making.
- Custom AI Development – Build intelligent applications tailored to your business needs.
- AI Model Optimization – Seamlessly switch between AI models with automated cost, accuracy, and performance comparisons.
- AI Automation – Automate repetitive tasks and free up time for strategic growth.
- Advanced Security & AI Governance – Ensure compliance, fraud detection, and secure model deployment.
Want to unlock the power of AI with enterprise-grade security and efficiency? Get Started with Avahi’s AI Platform!





