Cloud computing has become a cornerstone of business operations, offering unparalleled scalability, flexibility, and innovation. However, as organizations increasingly rely on cloud services, managing and optimizing cloud costs has become a huge challenge. Gartner reports that over 70% of cloud costs are often wasted, highlighting the need for diligent monitoring and analysis.
Organizations must adopt a strategic approach to cloud cost analysis to address this challenge. This involves understanding the various cost components, monitoring usage patterns, and implementing best practices for cost optimization.
By doing so, businesses can ensure they get the most value from their cloud investments while avoiding unnecessary expenses. This blog will explore the fundamentals of cloud cost analysis and outline best practices for optimizing cloud expenditures.
What is Cloud Cost Analysis?
Cloud cost analysis is the systematic process of tracking and evaluating expenses related to cloud services. It involves monitoring expenditures on various cloud resources, identifying spending patterns, and comparing current costs against benchmarks.
This process helps businesses understand how they utilize cloud services, highlighting areas where money is being overspent and uncovering opportunities for cost savings. Cloud cost analysis provides a clear and detailed picture of a company’s expenses, enabling smarter and more cost-effective use of cloud resources.
Why is Cloud Cost Analysis Important?
Cloud cost analysis is crucial in ensuring a business’s cloud usage aligns with its objectives. Offering detailed insights into cloud expenditures helps organizations understand how resources are used in relation to their goals. This understanding allows for strategic adjustments, ensuring that cloud investments are effective and efficient. The important benefits include:
- Enhanced Visibility: Cloud cost analysis provides a comprehensive view of cloud spending, enabling a better understanding of how resources are utilized.
- Cost Optimization: It helps identify areas of excessive spending, allowing businesses to implement cost-saving measures and optimize cloud usage.
- Accurate Budgeting and Forecasting: It facilitates the analysis of current usage trends, aiding in precise budgeting and predicting future cloud expenses.
- Reduction of Waste: Cloud cost analysis detects underutilized or idle resources, enabling the elimination of unnecessary costs and improving resource efficiency.
- Strategic Decision-Making: It offers valuable insights that support informed decisions regarding resource allocation and technology investments.
Understanding the Components of Cloud Cost Analysis
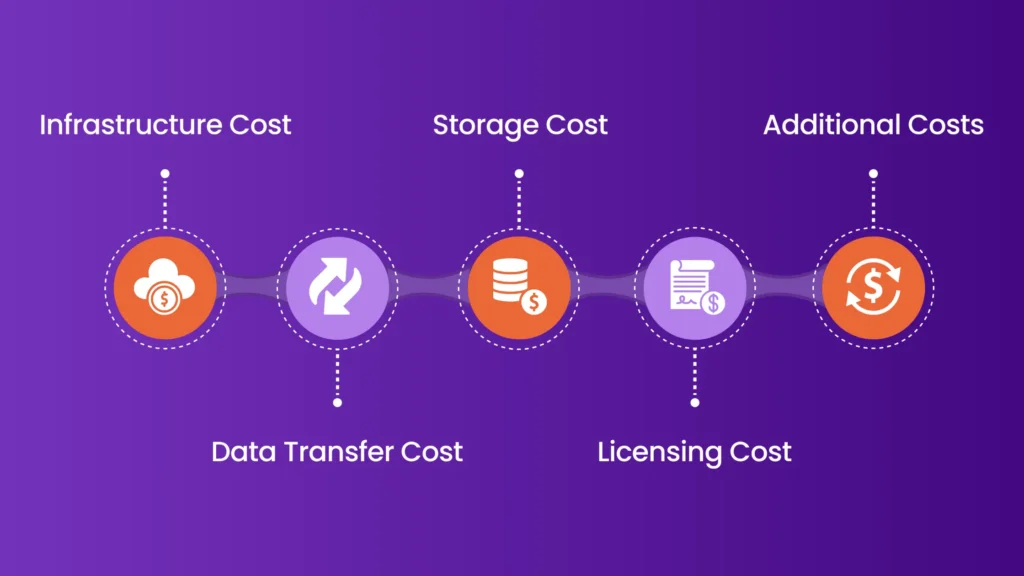
Cloud cost analysis involves examining various elements that contribute to overall cloud expenses. Businesses can better manage and optimize their cloud spending by understanding these components. Below are the important components of cloud cost analysis:
Infrastructure Cost
Infrastructure costs include expenses related to the core resources of cloud computing, including virtual machines, networking infrastructure, and containers. These costs are typically based on consumption and can be managed by:
- Understanding different pricing models such as on-demand, reserved, and spot instances.
- Analyzing how instance types and their usage impact costs.
- Calculating expenses related to virtual machines, CPU, and memory, as well as all infrastructure components like hardware, software, and networking.
Data Transfer Cost
Data transfer costs arise from moving data within and across cloud services or from on-premises systems to the cloud. These costs vary based on the volume of data, transfer distance, and type of service. Strategies to manage these costs include:
- Analyzing and improving data flow to reduce expenses.
- Using content delivery networks to manage data distribution.
- Employing services like AWS Direct Connect or Azure ExpressRoute to optimize data transfer costs.
Storage Cost
Storage costs pertain to maintaining data in various cloud storage services, such as object, block, and archival storage. These costs depend on data redundancy, retrieval frequency, and storage capacity. To manage storage costs, businesses should consider:
- Managing data storage efficiently through lifecycle policies.
- Employing different storage tiers based on data access patterns.
- Reducing storage costs by compressing data.
Licensing Cost
Licensing costs involve expenses for software and third-party services used in the cloud environment. These costs can be managed by:
- Reviewing terms and costs of software licenses.
- Ensuring efficient use of licensed software.
- Considering cost-effective open-source solutions.
Additional Costs
Additional costs in cloud computing may include expenses for services beyond basic infrastructure and support, such as:
- Costs associated with running serverless functions.
- Expenses related to machine learning operations.
- Fees for managed services that aid in cloud operations.
- Costs for meeting regulatory requirements and implementing security measures.
- Expenses for data backup solutions and disaster recovery plans.
How Can You Calculate Cloud Computing Costs?

There are certain questions that your business must consider before computing the costs:
- How much will the business spend on cloud resources?
- What are the costs associated with different services?
- Why has the bill increased recently? Is it due to business growth or platform inefficiencies?
- Should we create new budgets based on different engineering teams or product lines?
- Are there ways to optimize spending and enhance value?
These questions guide the analysis process and help focus on the most relevant metrics. Below, we will walk you through the essential steps to calculate cloud computing costs, ensuring a clear and thorough understanding of each component.
1. Define Your Requirements
Before you begin calculating costs, it’s crucial to understand your cloud migration needs comprehensively. Consider the workloads you’ll be running, performance objectives, data storage requirements, and regulatory compliance mandates. A clear grasp of these requirements helps develop accurate cost estimates and ensures that the cloud solution meets your specific business needs.
2. Select the Right Service Model
Choosing the appropriate cloud service model is essential. Options include
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS),
- Platform as a Service (PaaS), and
- Software as a Service (SaaS).
Each model offers different functionalities and pricing structures. Evaluate scalability, adaptability, and management overhead to determine which model aligns best with your financial and operational requirements.
3. Determine Resource Requirements
After selecting a service model, identify the resources needed for your cloud workloads. This includes CPU, RAM, storage capacity, and network bandwidth. Consider peak usage hours, anticipated growth, and redundancy needs. Accurately determining these resources ensures you can project costs more precisely and avoid unexpected expenses.
4. Understand Pricing Models
Familiarize yourself with the pricing options provided by your cloud provider. Most providers offer a pay-as-you-go model, charging based on actual usage. Additionally, there are options for reserved instances and volume discounts for recurring usage. Understanding these pricing tiers, discounts, and billing cycles helps you make cost-effective choices.
5. Calculate Usage Costs
Utilize your cloud provider’s pricing tools and online calculators to estimate usage costs. Enter your resource requirements and consumption patterns to get accurate cost estimates. Consider factors like instance type, storage options, and data transfer volumes. These tools clearly show expected expenses, helping you budget effectively.
6. Analyze Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Evaluate the total cost of ownership (TCO) by comparing the expenses of running workloads in the cloud versus on-premises infrastructure. Include direct and indirect costs such as hardware, software licenses, maintenance, and operational overhead. Analyzing TCO enables you to make informed decisions about your business’s most cost-effective deployment option.
7. Understand Your Cloud Bill
Cloud billing data can be complex, with numerous charges for data transfer, storage, and computing instances. To optimize costs, thoroughly analyze your current cloud bill to understand where money is spent. Look for
- resource usage,
- rate charges,
- and metadata attributes like project or account.
This granularity lets you detect small changes and address issues before they escalate into significant expenses.
8. Compare Value vs. Cost
Cloud cost analysis is not just about cutting costs but maximizing value. Evaluate how much it costs to provide your main services through the cloud and explore ways to optimize spending per unit. Focus on the efficiency and effectiveness of your cloud investments to ensure you get the maximum value for every dollar spent.
9. Leverage Reserved Instances (RIs)
AWS EC2 Reserved Instances can offer significant savings for applications with stable usage patterns. However, be mindful of potential drawbacks, such as predicting long-term usage and the commitment to capital costs. Best practices include buying reserved capacity for always-running instances and centralizing RIs for shared use across teams.
10. Optimize Data Transfers
Data transfer costs can add up quickly. Create a strategy to manage data transfers efficiently. When possible, keep data within the same availability zone or region, use less expensive regions for transfers, and leverage content delivery networks (CDNs) to reduce costs while maintaining fast delivery.
11. Reduce EBS Costs
Amazon Elastic Block Storage (EBS) costs can be managed by identifying detached and underutilized volumes, optimizing their size and type, and managing EBS volumes attached to stopped EC2 instances. Creating EBS snapshots for stopped instances can also significantly lower costs.
You can perform a thorough and accurate cloud cost analysis, enabling you to optimize expenses and make informed decisions for your business’s cloud strategy.
Best Practices in Cloud Cost Analysis
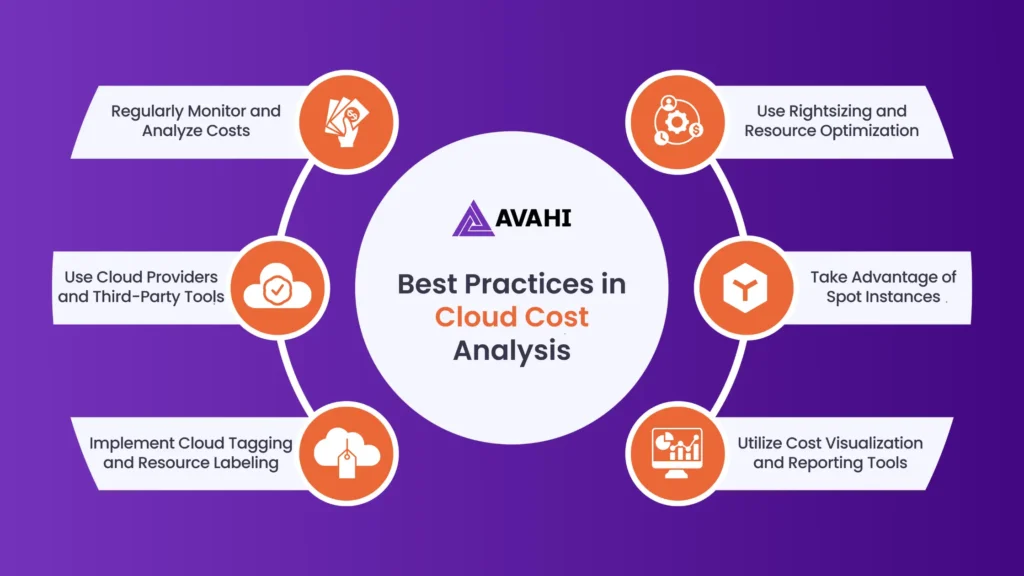
Effective cloud cost analysis is essential for optimizing cloud expenses and ensuring efficient resource utilization. Here are six best practices to help you get the most out of your cloud cost analysis:
1. Regularly Monitor and Analyze Costs
Continuous monitoring of cloud costs is crucial for identifying spending trends and patterns. Reviewing your budget regularly and setting up alerts for significant expense changes can help you spot opportunities for cost savings. Use cloud cost monitoring tools to keep track of costs and ensure that any unexpected spikes are quickly addressed.
2. Use Cloud Providers and Third-Party Tools
Cloud providers like Microsoft Azure and AWS offer various tools to help organizations understand and optimize their cloud costs. These tools can provide valuable insights into your spending patterns. If you need a more comprehensive view, especially in a multi-cloud environment, consider using third-party tools that integrate data from different platforms, offering detailed analytics and cost optimization recommendations.
For more information on these tools, refer to our detailed blog on Top 10 Cloud Cost Optimization Tools in 2024
3. Implement Cloud Tagging and Resource Labeling
Cloud tagging and resource labeling involve adding metadata or descriptive names to cloud resources, making tracking and identifying usage easier. This practice helps allocate costs accurately and provides better insight into resource ownership and cost drivers.
For example, AWS offers “Cost Allocation Tags,” which allow you to monitor your AWS expenses on your monthly bill, similar to writing notes on your resources. By understanding which departments, applications, or projects are using the most resources, you can make informed decisions on where to optimize cloud usage.
4. Use Rightsizing and Resource Optimization
Rightsizing ensures that you are paying for resources that match your actual usage. Adjusting the configuration and size of cloud resources to reflect actual needs can lead to significant cost savings. Resource optimization involves efficiently using your existing resources, such as automatically scaling resources up or down based on demand and distributing traffic across servers to balance loads.
5. Take Advantage of Spot Instances
Spot instances provide unused cloud resources at a discount but come with the risk of interruptions. By identifying stable usage patterns and incorporating these instances where appropriate, you can reduce costs while maintaining flexibility.
6. Utilize Cost Visualization and Reporting Tools
Visualizing cloud costs can help you better understand spending patterns and facilitate team communication. Cloud cost visualization tools can help you create dashboards and generate reports highlighting key metrics. These tools can help you identify cost drivers, track trends, and make data-driven decisions to optimize cloud expenses.
By following these best practices, you can effectively manage and optimize your cloud costs, ensuring that your resources are used efficiently and your budget is spent wisely.
Maximize Your Cloud Savings with Avahi

Transform how you manage and optimize cloud costs with Avahi‘s AWS Cloud Cost Optimization Service. Our team of experts helps you reduce the cost of running your cloud infrastructure while enhancing performance and resource utilization.
With our comprehensive approach, including right-sizing, increased elasticity, and smart pricing models, we’re committed to maximizing your cloud ROI. Discover how our tailored solutions can transform your AWS experience and propel your business forward.
Ready to significantly reduce your AWS costs and optimize your cloud infrastructure?